4. Project & System Definition
Phase B: Project Definition

4.2 Project Definition
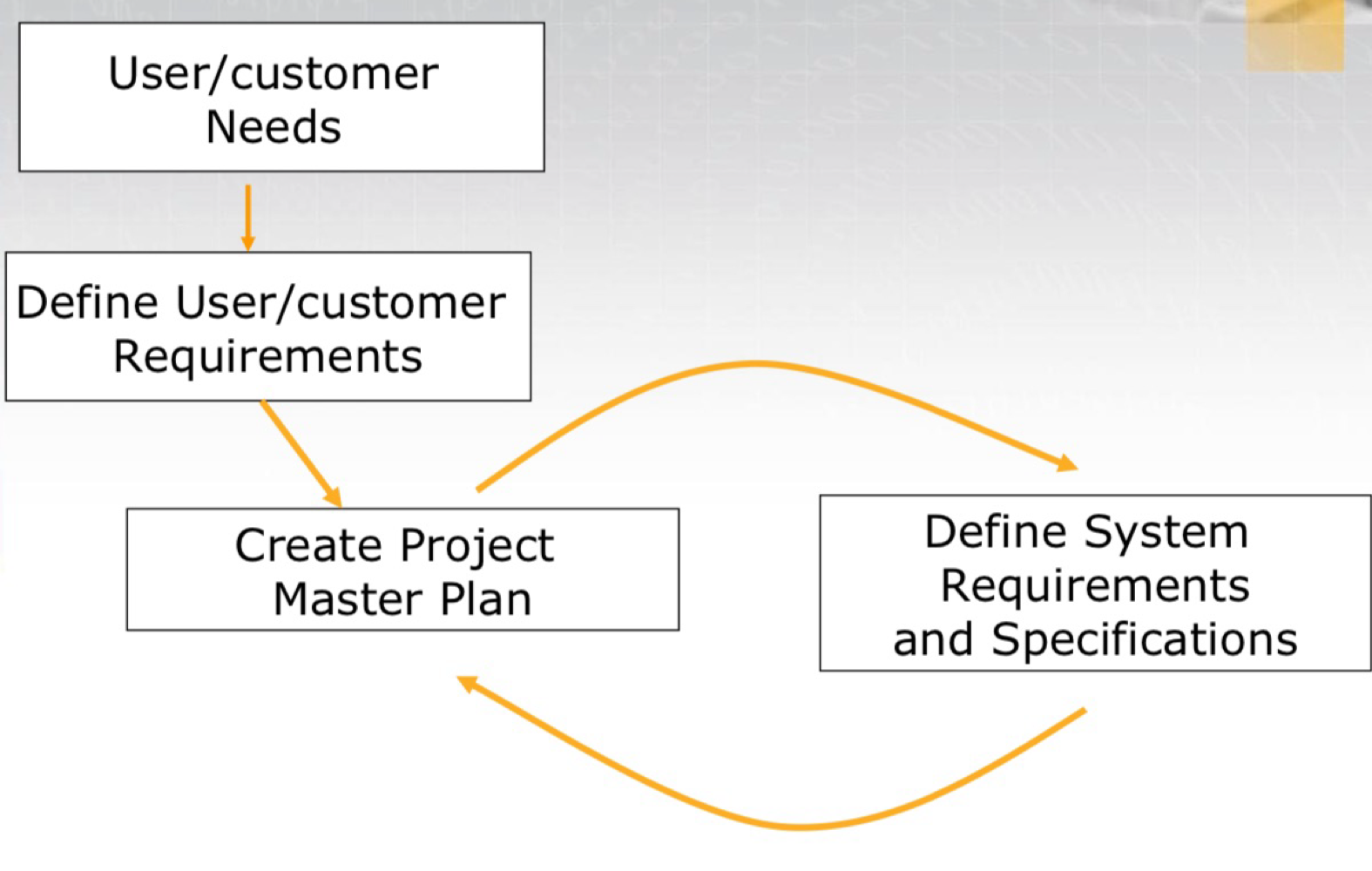
• During Definition, the project master plan and end-item requirements and specifications are defined.
• The system requirements and specification address “what” the end-item of the project must do.
• The project master plan describes “how” project will deliver end-item that meets system requirements and specifications
• Iterative process
- Details of the specifications are defined; master plan is expanded to reflect details
- As master plan is expanded, project constraints/opportunities/resources are identified, which leads to revisions in specifications
Primary Definition Tasks
Project Master Plan
• Project master plan addresses these questions to the satisfaction of project core team (people who will do work)
• Addresses all matters about project in sufficient detail for managers to organise and direct work to meet performance, cost, and time targets and for team to begin work
• Level of detail in the master plan far exceeds level in the proposal
Common Elements of Project Master Plan
-
What? Scope Statement, Charter, or SOW
-
What? Detailed requirements
-
How? Detailed work definition (WBS or PBS and work package/work task details)
-
Who? Responsibility for work tasks
-
When? Detailed schedules with milestones
-
How much? Project budget and cost accounts
-
What if? Risk plan
-
==How well, what, how? Performance tracking and control
-
Other elements of the plan, as needed for, • Work review and testing • Quality control • Documentation Implementation • Communication/meetings • Procurement • Contracting and contract administration
4.3 Phased Project Planning
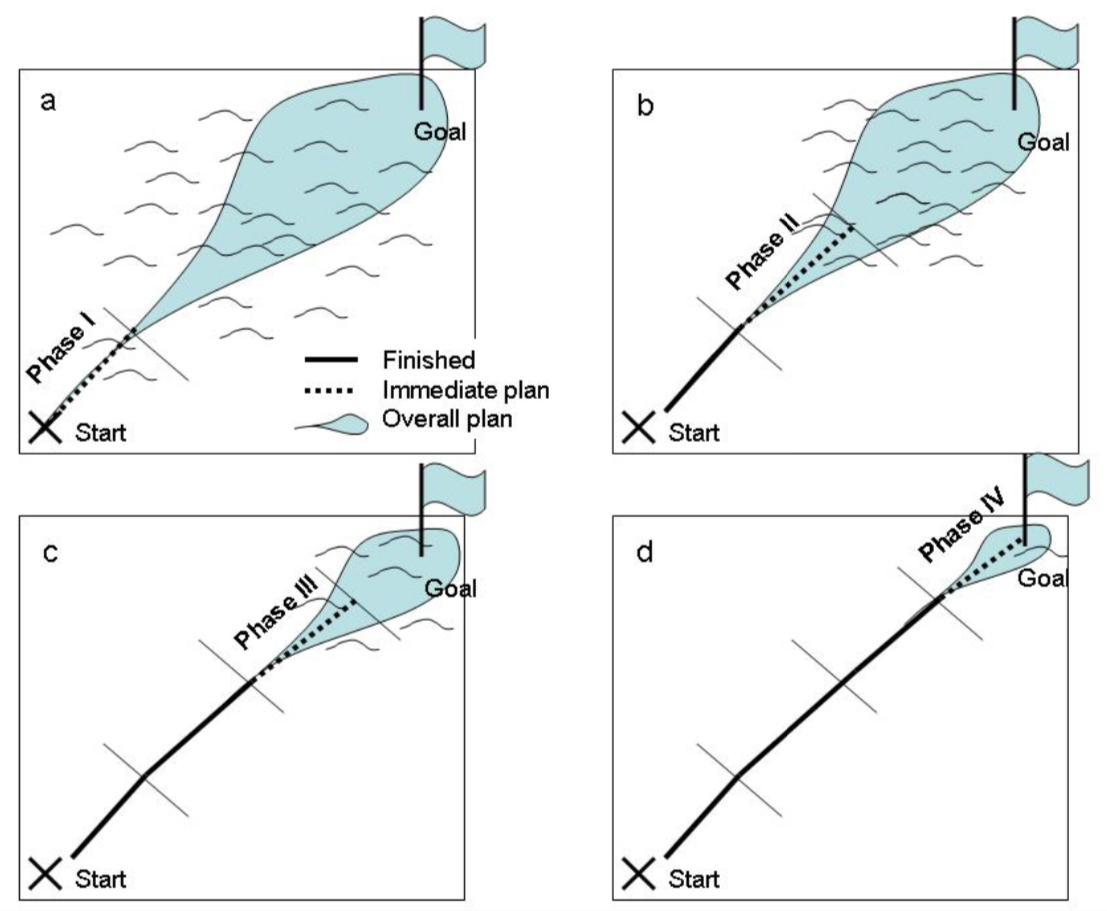
-
At the start of the project, often there are too many unknowns, so the plan must be developed in phases
-
The initial plan is somewhat rough though adequate to
- estimate project resources, time, and cost
- explain all this to the customer
-
As the project progresses,
- the unknowns decrease
- details of the plan are filled in
- a more-detailed plan is created for the next most immediate
- phase of the project
-
As project moves through the successive phases and stages, detailed plans are prepared with more-specific deliverables and schedules.
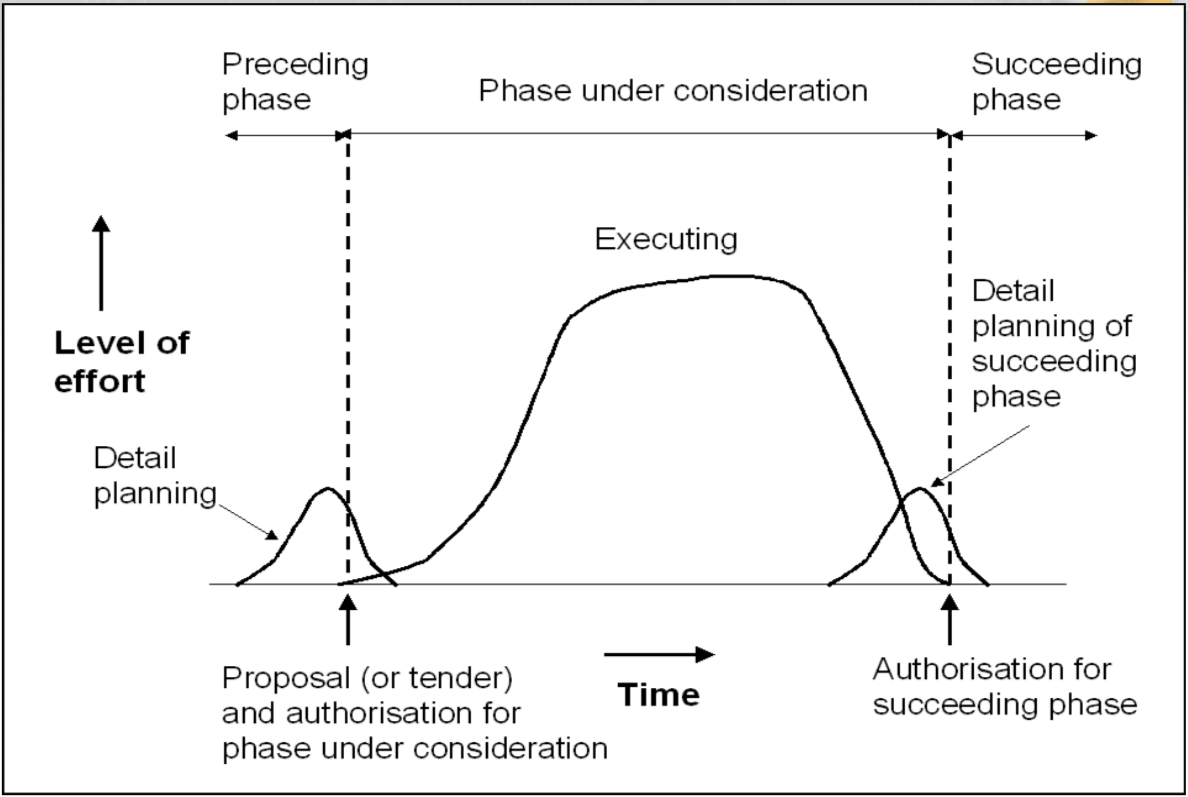
-
Sometimes each phase concludes with a milestone
- The customer or management review the deliverables and project performance
- If satisfied, they approve the deliverables and pay for work done thus far.
-
They also review the detailed plan for the next phase,
- If satisfied they authorise the next phase.
-
Authorisation to begin the next phase represents a commitment by the customer and management to support the phase
-
If the project has to be terminated, it is terminated at the end of a phase.
4.4 Systems Definition
-
System requirements and specifications elaborate in detail on the technical performance of end-item
-
Tell designers and builders what project end-item (deliverable) must be and do
-
Are a translation of user requirements into technical requirements
-
Users are ignorant of most system requirements
Problems with Requirements Definition
1. Incorrect Requirements: Wrong Needs
- Incorrect Definition of Needs
- Shifting or Vagueness of Needs
- Needs of Wrong User
- Conflicting Needs of Multiple Users
- Distortions of Needs by Experts
2. Imprecise or Ambiguous Requirements: (Subject to Multiple Interpretations)
- Human Language
- Deliberate Imprecision for Flexibility
- Nebulous Projects
- User’s Lack of Expertise
- Project Planner’s Oversight
3. Shifting Requirements:
- User’s Change of Mind
- Insurmountable Obstacles
- New Opportunities
- Seeking Perfection
4. Over-Specification of Requirements:
- Initiative Discouraged
- Requirements Ignored
- Insufficient Information
5. Under-Specification of Requirements:
- Chaotic project planning resulting in cost and schedule overruns
Guidelines for Defining User Requirements
-
State each requirement clearly; have both user and project staff sign-off on it
-
Assume if a requirement can be misinterpreted, it will be misinterpreted
-
Accept that changes to project are inevitable and things will not go precisely as planned
-
Include pictures, graphs, models, and other nonverbal exhibits in requirements formulation
-
Carefully monitor changes to requirements once project has begun
-
Educate both user and project staff about problems associated with specifying requirements
Requirements Definition:
-
A functional requirement is a kind of system requirement. It specifies the functions the end-item system must perform to meet the user requirements
-
Associated with functional requirements are performance requirements that specify the required level of performance.
Project and System Definition:
How do you keep everyone in the project focused on those requirements?
How do you develop a project plan that will be able to account for those requirements?
A. Make the system and project definition a team effort
incorporate the perspectives of everyone with a stake in the project
- customers, suppliers, functional areas such as engineering, marketing, manufacturing, customer service, and purchasing, and users and operators.
B. The more these individuals and groups have a hand in defining requirements and the plan, better the system requirements will account for their needs throughout the systems life cycle
• Common team approaches in Definition are Concurrent Engineering (chapter 13) and QFD.